Codeforces Round 746 Div 2 Editorial Solutions A - D
Gamer Hermose
Program Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define fast ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define ll long long int
#define dbg(a,b,c) cout<<a<<" "<<b<<" "<<c<<endl;
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define endl "\n"
#define INF 1e18
#define w(t) cin>>t;while(t--)
#define kill(a) {cout<<a<<endl;continue;}
#define pi 2 * acos(0.0)
int t,ans=0,tot=0,kk=0;
const int mxn=2e5+10,mod=1e9+7;
signed main()
{
w(t)
{
ll n,m,a,b,c,d,e,i,j,k,sm=0,sm1=0,cn=0,cn1=0,mx=-1e9,mn=1e9;
string s,ss,sr,sa;
bool f=false,ff=true;
cin>>n>>m;
ll ar[n];
for(i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>ar[i];
sort(ar,ar+n,greater<ll>());
sm=ar[0]+ar[1];
cn=m/sm;cn1=cn;
cn*=2;
m-=(cn1*sm);
if(m>0)
{
cn++;
m-=ar[0];
if(m>0)cn++;
}
cout<<cn<<endl;
}
}
Hermose Shopping
Program Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int > pii;
const int N = 1e5+10;
pii a[N];
int b[N];
int n, x;
int finda(int x) {
return lower_bound(b, b+n, x) - b;
}
int findb(int x) {
return upper_bound(b, b+n, x) - b;
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T -- ) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &x);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) scanf("%d", &a[i].first), a[i].second = i;
sort(a, a+n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) b[i] = a[i].first;
int flag = 1;
for(int i = 0; flag && i < n; i++) {
int idx = a[i].second;
int aa = finda(a[i].first), bb = findb(a[i].first) - 1;
if(aa <= idx && idx <= bb) continue;
if(idx >= x || n-1-idx >= x) continue;
flag = 0;
}
if(flag) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
return 0;
}
Bakery and Partitioning
Bakry faced a problem, but since he's lazy to solve it, he asks for your help.
You are given a tree of n nodes, the i-th node has value ai assigned to it for each i from 1 to n. As a reminder, a tree on n nodes is a connected graph with n−1edges.
You want to delete at least 1, but at most k−1 edges from the tree, so that the following condition would hold:
Is it possible to achieve this condition?
Output
For each test case, you should output a single string. If you can delete the edges according to the conditions written above, output "YES" (without quotes). Otherwise, output "NO" (without quotes).
You can print each letter of "YES" and "NO" in any case (upper or lower).
Note
It can be shown that the objection is not achievable for first, third, and fifth test cases.
In the second test case, you can just remove all the edges. There will be 5 connected components, each containing only one node with value 3, so the bitwise XORs will be 3 for all of them.
In the fourth test case, this is the tree: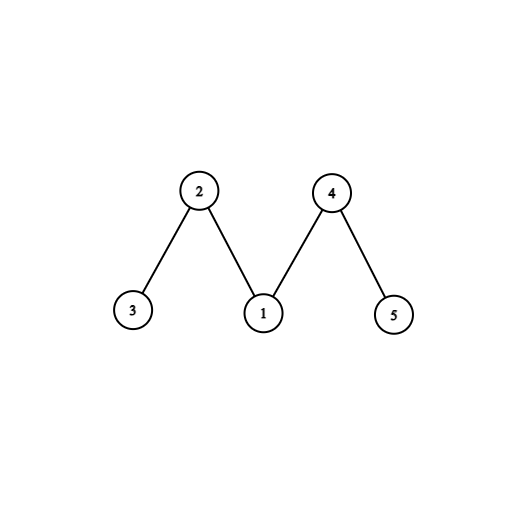 .
.
You can remove an edge (4,5)
The bitwise XOR of the first component will be, a1⊕a2⊕a3⊕a4=1⊕6⊕4⊕1=2 ( )⊕ denotes the bitwise XOR).
The bitwise XOR of the second component will be, a5=2.
Program Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define nl '\n'
vector<vector<int>> g;
vector<ll> a;
ll all;
int k;
ll dfs2(int v, int par, int bad, bool& good, ll val) {
ll res = a[v];
for(int ne : g[v]) {
if(ne == par || ne == bad) {
continue;
}
res ^= dfs2(ne, v, bad, good, val);
}
ll rest = all;
if(rest == res && res == val) {
if(par != -1 && k >= 3) {
good = true;
}
}
return res;
}
ll dfs(int v, int par, bool& good) {
ll res = a[v];
vector<ll> vec;
for(int ne: g[v]) {
if(ne == par) {
continue;
}
vec.push_back(dfs(ne, v, good));
res ^= vec.back();
}
ll rest = all ^ res;
if((rest == res)) {
if(par != -1) {
good = true;
}
}
else if((res == all) && (rest == 0)) {
if(par != -1) {
bool good2 = false;
dfs2(0, -1, v, good2, res);
if(good2) {
good = true;
}
}
}
return res;
}
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n >> k;
g.clear();
a.clear();
a.resize(n);
all = 0;
g.resize(n);
set<int> ss;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
all ^= a[i];
ss.insert(a[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
u--, v--;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
bool ok = false;
dfs(0, -1, ok);
cout << (ok ? "Yes" : "No") << nl;
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
Hermose in ICPC
Program Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define task "sol"
#define lb lower_bound
#define ub upper_bound
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define mp make_pair
#define zs(v) ((int)(v).size())
#define BIT(x, i) (((x) >> (i)) & 1)
#define CNTBIT __builtin_popcountll
#define ALL(v) (v).begin(),(v).end()
//#define endl '\n'
typedef long double ld;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
const int dx[4]={-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4]={0, 1, 0, -1};
const int dxx[8]={-1, -1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1}, dyy[8]={0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1};
const ll mod = 1000000007; /// 998244353
const ll base = 331;
const int N=3005;
pii e[N];
int n;
int cnt=0;
int numE;
vector<int> dsk[N];
int query(vector<int> &res)
{
cnt++;
assert(cnt<=12);
cout<<"? "<<zs(res)<<' ';
for (int i:res) cout<<i<<' ';
cout<<endl;
int x;
cin>>x;
return x;
}
int query(int l, int r)
{
assert(l<=r);
vector<int> res;
for (int i=l;i<=r;++i)
{
res.pb(e[i].fi);
res.pb(e[i].se);
}
sort(ALL(res));
res.resize(unique(ALL(res))-res.begin());
return query(res);
}
void dnc(int l, int r, int ans)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if (l<=0||r>n-1||l>r) return;
if (l==r)
{
if (cnt<12) assert(ans==query(l,l));
cout<<"! "<<e[l].fi<<' '<<e[l].se<<endl;
exit(0);
}
int res=query(l,mid);
if (res==ans)
{
dnc(l,mid,ans);
}
else
{
dnc(mid+1,r,ans);
}
assert(1==0);
}
void dfs(int u, int pre)
{
for (int v:dsk[u]) if (v!=pre)
{
e[++numE]=mp(u,v);
dfs(v,u);
}
}
void solve()
{
cin>>n;
for (int i=1;i<=n-1;++i)
{
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
dsk[u].pb(v);
dsk[v].pb(u);
}
dfs(1,1);
vector<int> vec;
for (int i=1;i<=n;++i) vec.pb(i);
int ans=query(vec);
dnc(1,n-1,ans);
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0);
solve();
}
Links
More about Codeforces Round 746 Div 2
Codeforces organizes many contests out of which one is this Codeforces rounds to improve coding skills and get a higher coding knowledge. Codeforces Round 746 Div 2 was too a great round to test our coding skills. This round was held on
Sunday, October 3, 2021 at 20:05UTC+5.5. This round will be rated for coders with rating upto 2100. A total of 6 problems are given which needs to be solved in 2 hours 15 minutes.
The first problem that is Gamer Hermose was cakewalk it was so simple that in 5 minutes we had more that four thousand successful submissions. Problem B was too a great deal of simplicity but it took a bit of time to understand what to do in the problem. Problem C was medium level and was a good question of logic for the average coders and for best coders it was just too simple. Problem D was good to go but the question was quite difficult to guess what algorithm would be required. Problem E1 was quite simple and many successful submissions were made. Problem E2 and F were the testing the skills of top coders and average coders just kept guessing what algorithms to use.
The contest was a great success and every body enjoyed it truly. Just practice more questions and go ahead in building a streak of code and get better everyday. Happy coding journey ahead.
 .
.
Comments
Post a Comment